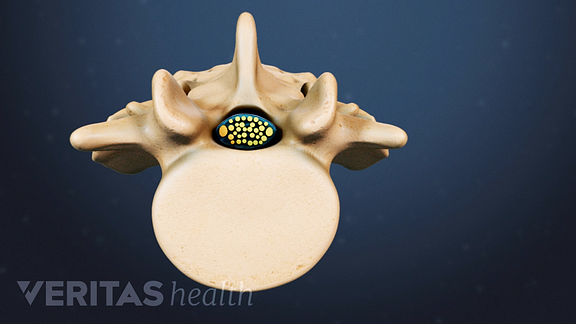
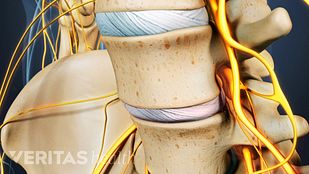
Degenerative changes in the spinal tissues associated with aging result in the vast majority of lumbar spinal stenosis diagnoses.1,2一个comprehensive evaluation of the potential sources is important for an accurate diagnosis of this condition.
椎管狭窄引起的脊髓神经的空间的收缩。看:腰椎管狭窄症Video
Common Causes of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
一个ging-related degeneration may affect the spinal joints, ligaments, and/or the intervertebral discs, causing the following changes2:
Hypertrophy of facet joints
一个rthritic degeneration may cause the facet joints to become arthritic and grow bone spurs (overgrown bone) that may impinge on spinal nerve roots and/or the spinal cord.
看到Bone Spurs (Osteophytes) and Back Pain
Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum
Thickening of the short bands of ligament that connects the inner surface of the spinal canal may compress the spinal cord.
Degeneration of discs
Degeneration can cause a decrease in the height of intervertebral discs, reducing the disc space and narrowing the bony openings for spinal nerves (intervertebral foramen). Degeneration may also cause碟片疝,compressing spinal nerve roots, and/or the spinal cord.
看到What Is Degenerative Disc Disease?
Degenerative spondylolisthesis
在椎骨中年龄相关的变化也可以在运动节段内引起不稳定,从而导致在其下方的一个椎体的打滑。
看到滑脱
One condition may lead to the other, for example, a reduction in disc height may cause a bulging or buckling of the ligamentum flavum into the back of the spinal canal.
Less Common Causes of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Rarely, the following conditions may cause spinal stenosis in the lower back:
- Inherited or genetic,如短椎弓根(即在后面在前面连接椎体的拱椎骨的一部分)2
- Complications after lumbar surgery,如laminectomyorlumbar fusion2
- Systemic conditions,如佩吉特氏病2
- Spinal growths,如tumors,囊肿,或脓肿在下部脊柱(脓的集合)
腰椎管狭窄症的风险通常随着年龄的增加而增加。风险因素还包括遗传倾向,体重超标,涉及重体力劳动的职业。1
在这篇文章中:
Diagnosis of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
一个doctor can diagnose stenosis in the lumbar spine based on specific clinical presentations and through medical imaging tests. Conducting a physical exam and reviewing the medical history helps a doctor determine the pattern of symptoms. Medical imaging tests help determine the location and severity of stenosis.
Physical exam and review of medical history
医生通常会检查疼痛、麻木、音乐le reflexes, and nerve function in the legs. Specific elements of the physical exam will include one or more of the following:
- Romberg’s test.This test checks for spinal cord impairment. In this test, the patient stands without support, and with their eyes closed. A loss of balance indicates a positive test result and may signal spinal cord damage or severe lumbar nerve root compression between L4-L5 and/or L5-S1.3
- 步态测试。In this test, the doctor analyzes the walking pattern of the patient to check for a wide-based or steppage gait, or loss of balance while walking.
- Neurological tests.These tests include analyzing the leg’s muscle reflex to check for nerve root compression in the lower back.
- Straight leg raise test.This test aims to access sciatic nerve root compression in the lumbar and/or sacral spine. During this test, the patient lies on their back and the doctor gently lifts the patient’s leg. If pain is experienced during this maneuver, the test is considered positive.
During a physical exam, the doctor also reviews the medical history, which includes information about the onset and duration of symptoms, past surgeries, medications, and the presence of concomitant medical conditions.
医学影像检查为腰椎管狭窄症
Imaging tests may be helpful in locating the site and severity of lumbar spinal stenosis and include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).一个n MRI is typically considered the gold standard test to identify spinal stenosis.MRI’sare sensitive in identifying the size, shape, and associations between tissues of the spine and can provide details of important structures, such as degenerated discs.4,五
- X光片。常规的x射线在识别骨折和椎骨的缺陷,则运动节段的对准,椎间盘高度损失和骨骨刺形成是有用的。4
- Computed tomography (CT) scans.一个CT scan提供了脊柱结构的可视化,并且当MRI不可用,或者可能可以进行。
- 脊髓造影:一个脊髓造影involves the injection of a radiographic dye into the spinal canal, which is followed by a CT scan. Myelograms are typically only performed in patients who cannot undergo an MRI or have had prior surgery.
It is important to understand that medical image findings may not always correlate with the symptoms. Up to 30% of adults older than 60 years may have imaging evidence of lumbar spinal stenosis with no symptoms.2 A history of clinical symptoms along with imaging evidence is essential to diagnose symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis.4
一旦腰椎管狭窄症被识别为患者的症状的原因,一个明确的治疗方案可配制。非手术治疗通常推荐了好几个星期被认为是外科手术之前。
References
- 1。Huang W, Zhou G, Zhang Y. Risk factors for ligamentum flavum hypertrophy in lumbar spinal stenosis patients from the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China: protocol for a retrospective, single-center study. Clinical Trials in Orthopedic Disorders. 2017;2(1):11.doi:10.4103/2542-4157.201057
- 2。Dixit R. Low Back Pain. In: Kelley and Firestein’s Textbook of Rheumatology. Elsevier; 2017:696-716.
- 3。Dydyk AM, M Das J. Radicular Back Pain. [Updated 2020 Apr 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546593/
- 4。劳瑞Ĵ,腰椎管狭窄症的Tomkins的巷C.管理。BMJ。2016年1月:h6234。DOI:10.1136 / bmj.h6234
- 5。Lee SY, Kim TH, Oh JK, Lee SJ, Park MS. Lumbar Stenosis: A Recent Update by Review of Literature. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(5):818–828.doi:10.4184/asj.2015.9.5.818